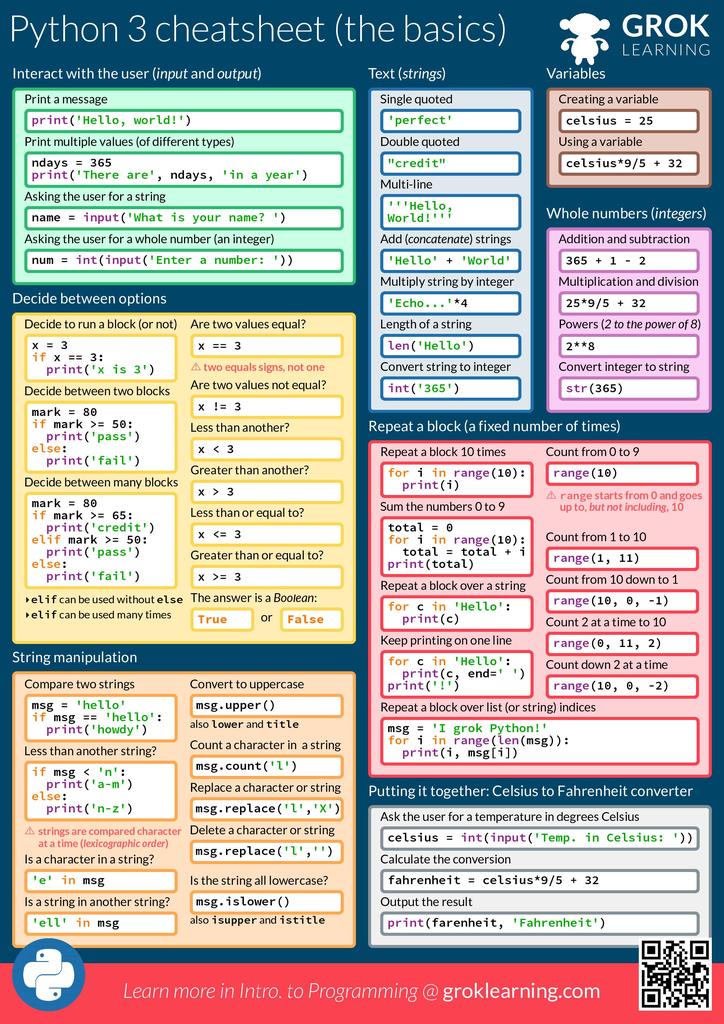
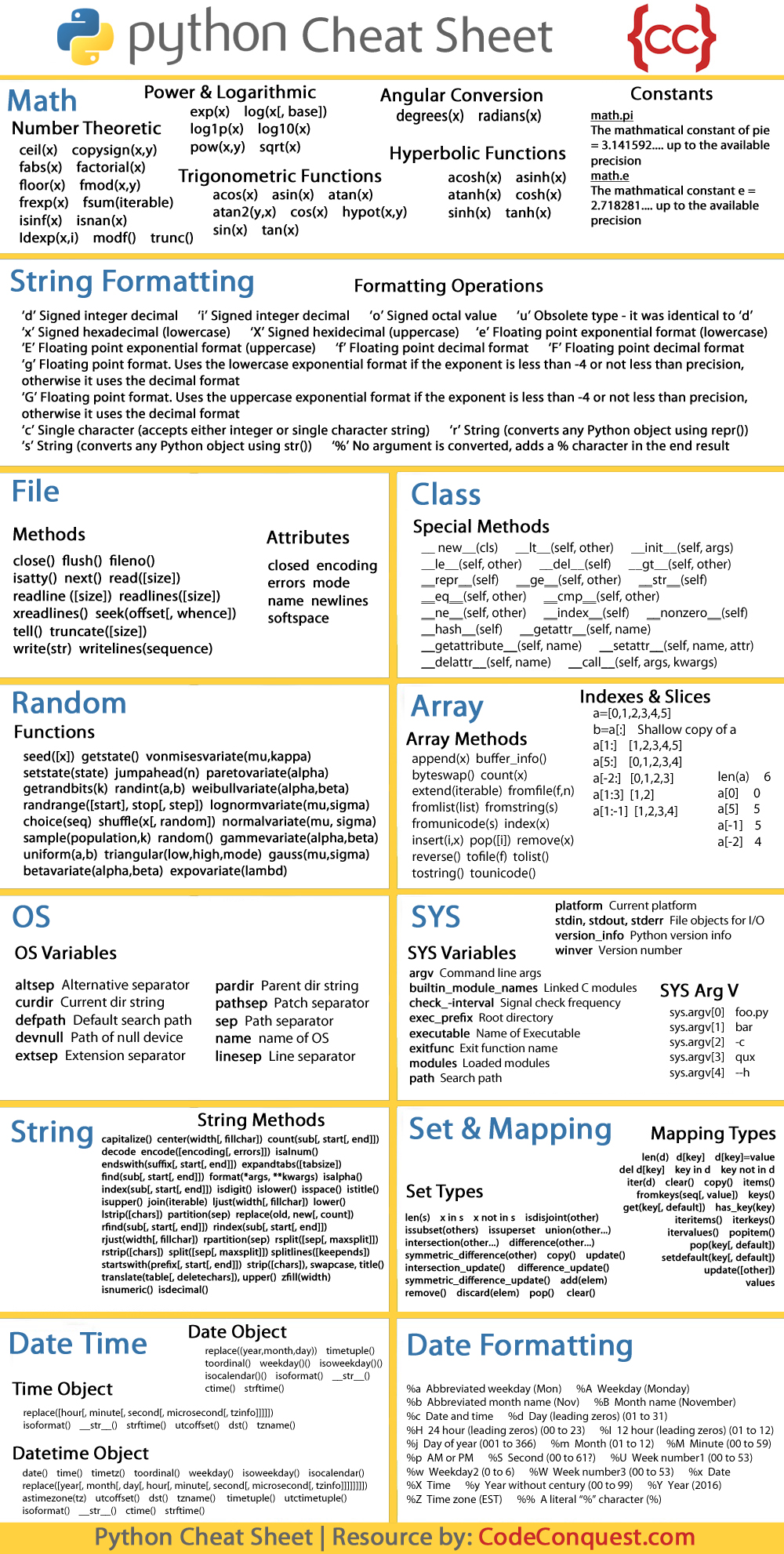
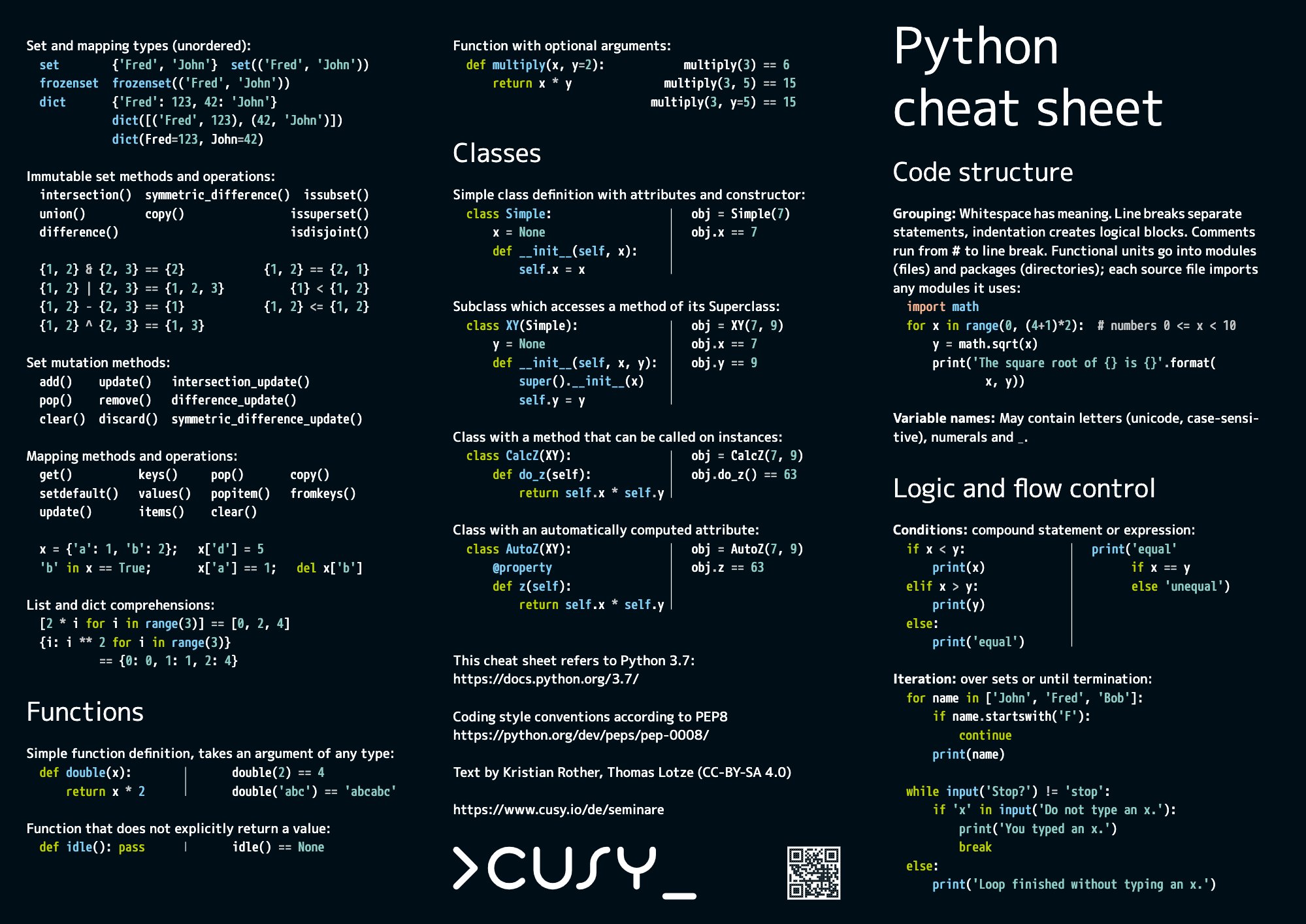
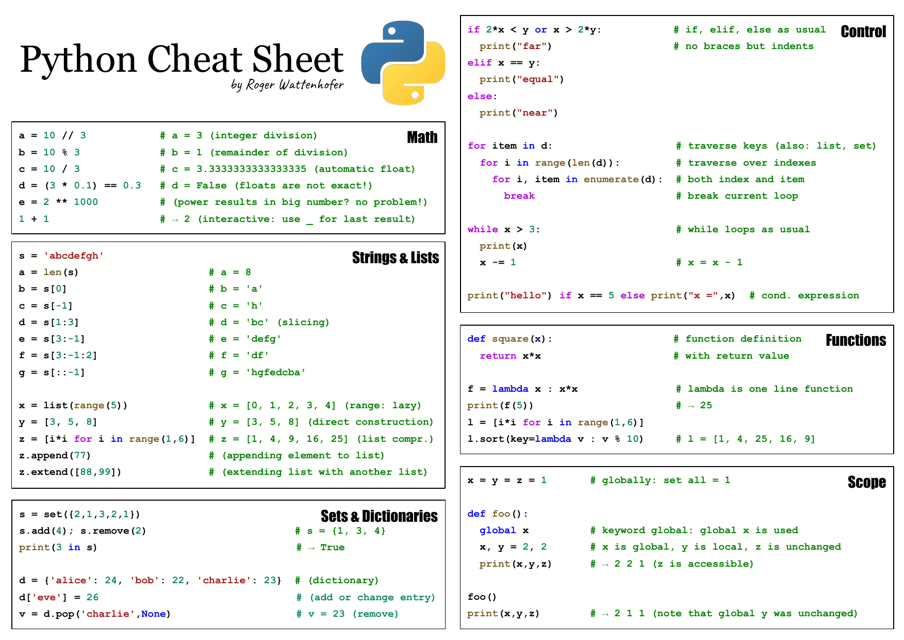
Cheat Sheet For Python - The input() function always returns data as a string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. The input() function always returns data as a string. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. The input() function always returns data as a string. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
Getting Started With Python Cheat Sheet Datacamp Bilarasa
Representation string of x for display (cf. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. The input() function always returns data as a string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function.
NumPy Cheat Sheet Data Analysis In Python DataCamp, 47 OFF
The input() function always returns data as a string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
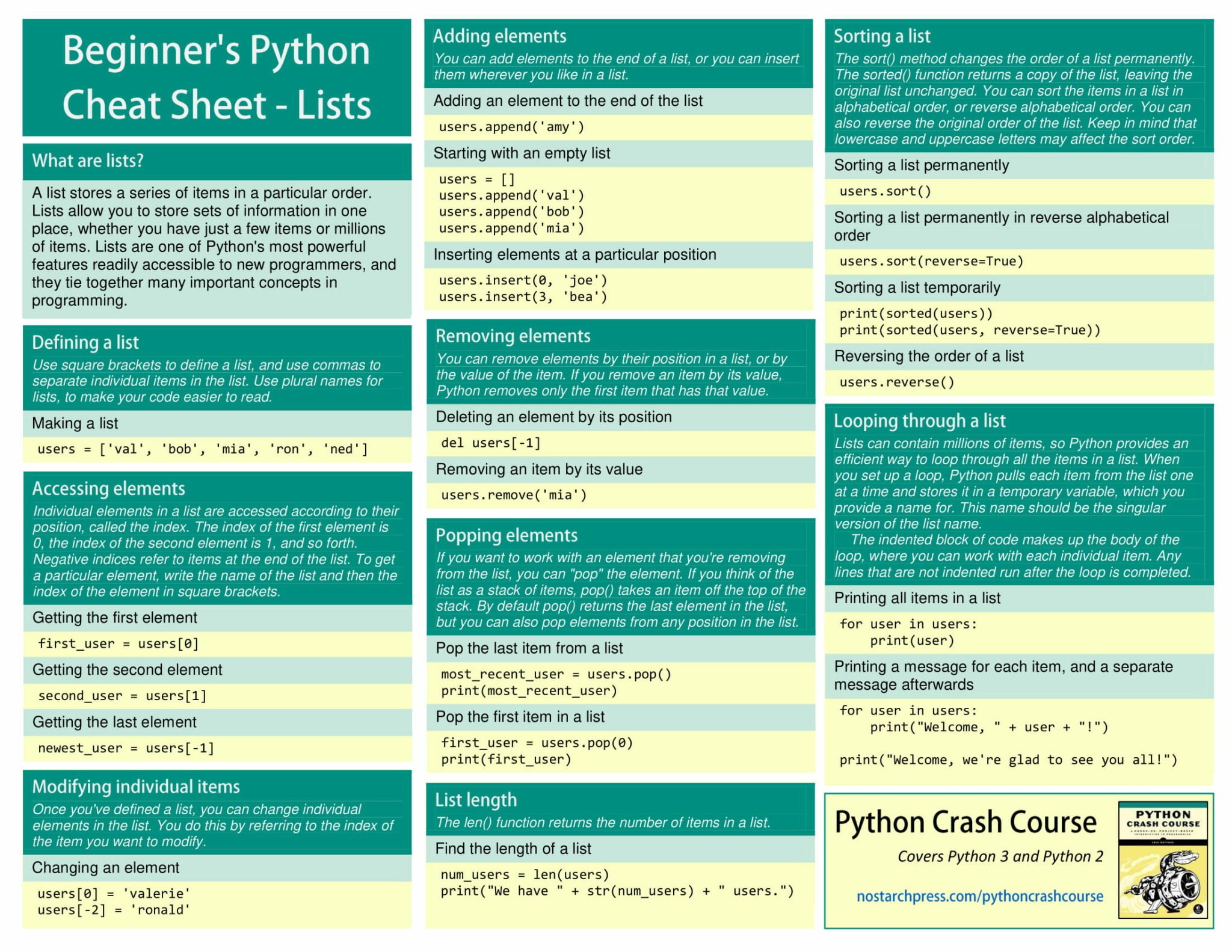
a poster with some type of text and numbers on the back ground
The input() function always returns data as a string. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. Representation string of x for display (cf.
Basic Python Programming Language Poster Cheat Sheet Teaching Resource
We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. The input() function always returns data as a string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
Printable Python Cheat Sheet
The input() function always returns data as a string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
pythoncheatsheet.jpg
Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. Representation string of x for display (cf. The input() function always returns data as a string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function.
BeginnersPythonCheatSheet8 (1) GlobalSQA
We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. Representation string of x for display (cf. The input() function always returns data as a string. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string.
Python Cheat Sheet Roger Wattenhofer Download Printable PDF
Representation string of x for display (cf. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. The input() function always returns data as a string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function.
Python Leetcode Cheat Sheet sheet
Representation string of x for display (cf. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. The input() function always returns data as a string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function.
Python Cheat Sheet for Beginners in 2024 Best Python Cheatsheet
Representation string of x for display (cf. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. The input() function always returns data as a string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function.
Formatting On The Back) = Variables Assignment Char Repr(X)→ . Literal Representation String.
The input() function always returns data as a string. Representation string of x for display (cf. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function.